Hair transplantation at a young age
It is generally believed that scalp hair loss occurs and characterizes large age groups of men. This view is fundamentally wrong. Hair loss can be a major problem for many young men affecting negatively their psychology and causing them to have low self-esteem. It is no coincidence that many young people who lose their hair have as their only thought the immediate restoration of their problem.
But is hair transplantation the best way to deal with this loss of hair growth at a young age and is there finally a suitable or proper age for someone to proceed with this operation?
The causes of premature hair loss
Thinning of scalp hair in men can appear from the very young ages of 17-20 years. The main and dominant cause is hereditary factors, specifically the early onset of androgenetic alopecia, the final progression of which occurs at different rates and to varying degrees over time.
However, there are many factors that can burden this hereditary predisposition to alopecia and accelerate its clinical manifestation. Such factors are physical or psychological stress, medication, hormonal disorders, pathological conditions, poor nutrition, environmental factors.
Is there an appropriate age for hair transplantation?
In theory, there is no minimum or maximum age for someone to proceed with a hair transplant. The general health of the person concerned, the diagnosis of alopecia and the potential of the scalp to support the operation are the necessary parameters that will be evaluated in order to perform the hair transplant safely and effectively.
What happens at young ages?
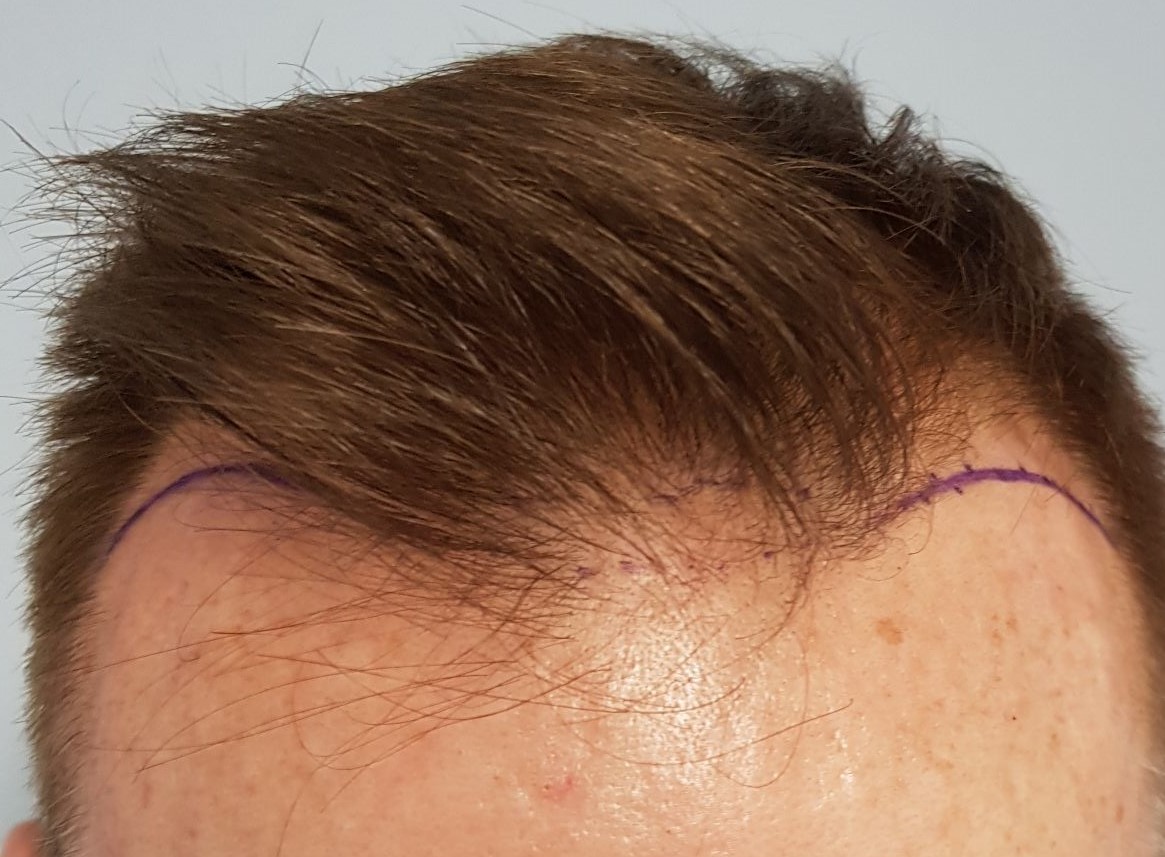
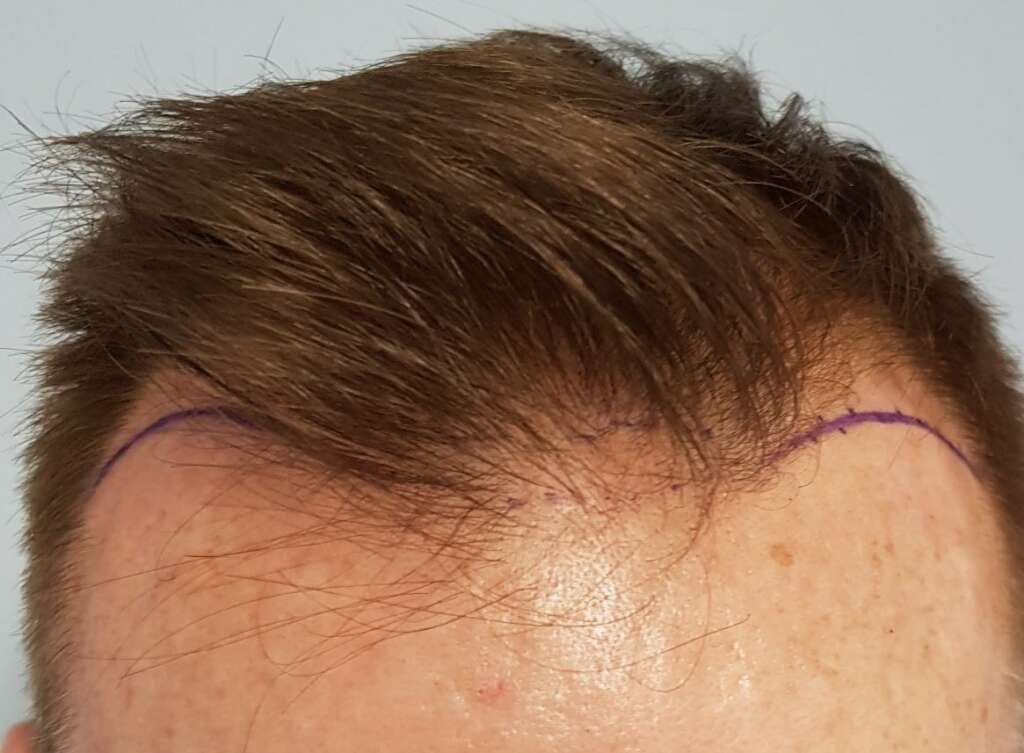
There are additional factors to consider for hair transplant at young ages (18-25 years). The most important are the explanation of the evolution of androgenetic alopecia over time and the respect by the doctor of the original hair growth to the greatest extent possible.
The doctor must be able to address the concerns and anxiety of the young person who is losing his hair by offering conservative hair loss treatments in order to keep his hair as long as possible but also by explaining to him the fatal final progression of androgenetic alopecia over time and how it sets rules in the plan of the invasive procedure should this be decided.
Androgenetic alopecia as a condition that evolves over time is affected by the physical and psychological health of the patient, which makes the rate of its development unpredictable. Also, in young men it is possible that the so-called donor area (the occipital part of the head from where the hair to be transplanted is extracted) may be affected to some extent and thus it may not be finally strong enough to restore either the entire extent of the alopecia area or a satisfactory restored hair density.
If a hair transplant is decided upon, it is very important not to be too invasive in terms of the number of hairs to be implanted. In such case there is a great possibility of either the premature exhaustion of the donor area or the premature loss of the existing hair, and therefore worsening of the patient’s problem, in the recipient area where the hair implantation was done.
Also, the restoration of the frontal hair line should be done with caution regarding its shape, its height as well as its connection with the temples. Finally, the patient must be explained the priority that must be followed regarding the order of restoration of the three zones of androgenetic alopecia, in order for a natural and aesthetically satisfactory result.
Hair transplantation or preservative treatment? Which is the correct choice?
It is not always wise for a young man to proceed with a hair transplant when he is in early stages of hair loss. Approved medication to enhance hair growth combined with appropriate nutrition or hair loss supplements if necessary, approved scalp care products, physical exercise, calmer lifestyle when possible, as well as treating any other health issues that aggravate hair loss, are the first approach to the agony of the young man who loses his hair.
Along the way, the patient’s response to the treatment process and therefore its effectiveness is evaluated and, if desired, hair transplant is decided. The plan of this transplant is the next important step which should be made with the future general image of the patient’s face and scalp in mind and not the past image of his teenage years.
In the case of premature or extensive hair transplantation without a long-term plan, the result, even if it may be immediately satisfactory, may ultimately betray the patient’s expectations in the long run as it can become unnatural and unsightly.
It must be emphasized that precisely because of the progression of androgenetic alopecia hair transplantation is an invasive procedure that will be repeated several times over time, which makes it even more necessary to respect and value the skin and hair growth of the head.
What should be done?
It finally seems that over time by individually monitoring the rate of development of androgenetic alopecia, the right combination of conservative strengthening of hair growth (which is essentially a lifelong commitment), and hair transplantation at the appropriate timing, is perhaps the ideal method so that the patient maintains a relatively stable overall scalp image that closely corresponds to the aging process and the changes in his face and general appearance.